Just as the 2001 Enron scandal led to the enactment of the Sarbanes-Oxley (SOX) legislation in the US, so major business failures in the UK ‒ such as the large contractor Carillion, the retailer BHS and Patisserie Valerie ‒ have hastened the Government’s decision to put SOX in place here. The aim is to ensure that management is reporting an accurate view of the business to the auditors and shareholders.
If your SAP® system is relied on for your financial reporting, then you must be certain that the information that it holds is a faithful reflection of the organisation’s real accounts. That means that all access to the system must be aligned closely to the user’s job functions and it must be regularly verified, to ensure the integrity and confidentiality of the data. This is, of course, also very much in line with the GDPR requirement of ‘Privacy by Design’, which needs to be applied when providing access to information systems such as SAP.
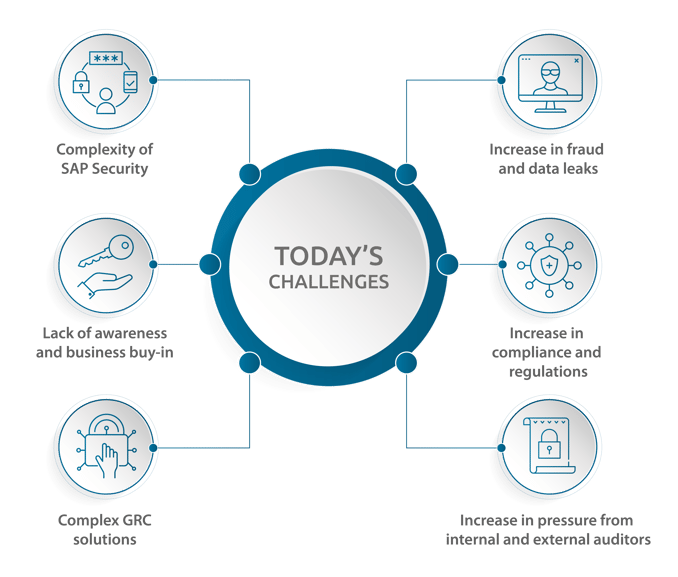
Brydon published a report “Restoring trust in audit and corporate governance” proposing guidelines to strengthen the UK framework for large companies and the way they are audited. The estimated date for these new rules to enter into force is December 2023. Here are the key findings from the report:
“The CEO and CFO must provide an annual attestation to the board of directors as to the effectiveness of the company’s internal controls over financial reporting and that this attestation be guided by new principles on internal controls reporting to be developed by the Audit Committee Chairs Independent Forum and endorsed by ARGA. [2.8.3] “.
“Companies will be required to disclose when any material failure of their internal controls has taken place. A disclosed failure would lead to the CEO/CFO attestation being subject to audit for the following three reporting years. [2.8.4] “.
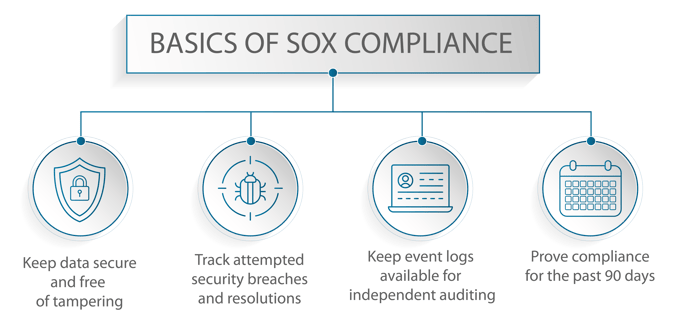
This means that manual processes such as excel spreadsheets will probably no longer be allowed. Companies using SAP will be invited to move their manual processes into automated GRC applications for SAP. UK SOX also means that the management team must quickly identify who made changes in the SAP systems and when.
Building the best GRC for SAP strategy for your organisation requires a flexible and business-centric tool with the following capabilities:
Identify access risks: The ability to identify SAP access risk exposure and show clean-up opportunities via a user-friendly web application.
Review access alignment: Check that users’ access is limited to what they actually need to do for their job and identify superfluous access.
Periodic review of users’ access: Allow your business users to review the SAP users’ access risk in your SAP systems periodically with ease and efficiency. This process will significantly improve the visibility of your GRC environment, and may be an audit and statutory requirement for your organisation.
Provide emergency access: When a user’s access is closely aligned to their daily job requirements, there may well be a need for temporary or emergency access for a limited period – often called firefighter access. You should be able to do this efficiently, and provide a complete audit trail.
Trust relationships: Allow monitoring of terminals where users login and the times, in order to discover anomalies that might indicate unauthorised or inappropriate use.
Provide full audit trail: Store a complete audit trail of all changes made to users’ access in the SAP system.
It should be remembered that the GRC tool is just one part of an overall GRC strategy that must be designed and implemented to ensure that all regulatory requirements can be met:
This strategy enables the GRC tool to do an effective job of maintaining and monitoring the SAP system.
Curious for more information? Find out about GRC for SAP solutions and request a demo.
Salomé is a Cloud and Security Marketing Specialist for Europe. She completed her master degree through Microsoft before joining the EPI-USE Labs team. Her goal is to research different challenges in the market and share SAP knowledge with the IT industry.