Missed the previous articles? Read them here: Article 1 | Article 2 | Article 3
It is official: we can't leave it all to the robots. The fourth article of our series on GDPR and POPIA is all about data analysis and automated decisions. Read on:
“First dates are interviews”
The dreaded first date. As if getting to this point isn’t harrowing enough, we now have to sit through an interview that may lead to some painful rejection. And let’s be honest, when we sit at a restaurant with this person, we are doing a fair bit of analysis on whether they are suitable mates or not. The end result of this analysis is a profile of the person who sits in front of us which may inspire us to either leave or get a follow-up date.
We do the same thing in business - when we get data on someone, we analyze it to extract value for our specific purpose that leads to some action.
Decisions inspiring actions
We use data either directly, or for analysis. Analysis of personal data may result in profiles that inspire action. Data analysis is either performed by hand or through automation. GDPR and POPIA address automated decision making that affects data subjects.
Automated decisions? Not on its own
In Section 71 the POPI Act states: “...a data subject may not be subject to a decision which results in legal consequences for him, her or it, or which affects him, her or it to a substantial degree, which is based solely on the basis of the automated processing of personal information intended to provide a profile of such a person including his or her performance at work, or his, her or its credit worthiness [sic], reliability, location, health, personal preferences or conduct.”
It is worth noting that consent is a prerequisite for POPIA when it comes to automated decision making. In Subsection 2 of Section 70 (emphasis added), it is stated that “A data subject must be given a reasonable opportunity to object…to request verification, confirmation or withdrawal of such information if the data subject has not initially refused such use.”
Article 22 of the GDPR is a near carbon copy: “The data subject shall have the right not to be subject to a decision based solely on automated processing, including profiling, which produces legal effects concerning him or her or similarly significantly affects him or her.”
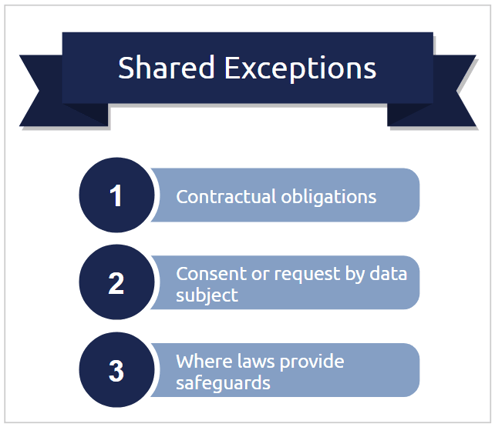
There are some shared exceptions in both GDPR and POPIA:
- Contractual obligations
- Consent or a specific request by the data subject
- Where a governing law enforces appropriate safeguards
In the hands of the data subject
Automated profiling is a sticky issue, especially when the data is of a sensitive nature. For example, a system registers that an individual was diagnosed with a terminal illness. The system uses health as an input for automated decision making that determines company promotions. As a result, this person may be unfairly profiled at their workplace as they are passed over for promotion.
Neither GDPR nor POPI explicitly prohibits automated decision making or profiling. Both laws are clear that it can’t be the only means to make a decision. Even though we can use automated decision making, the ultimate decision still needs human involvement.
Both GDPR and POPIA also provide the data subject with a right to contest the results of such processes or have their data excluded.
When it comes to developing a policy, give consideration to:
- The risk associated with data inputs as assumptions for a decision-making process
- The potential effects that such decision making may have on the data subjects
- The inclusion of one or more human controllers
- The right to object and request human intervention in such decisions
- A clear procedure to manage objections to the results of automated decisions
From a technical perspective:
- There should be a way to exclude individual records from automated processing.
- Fields that show objections should also be included
- Persistent overrides of automated outcomes should be implemented.
Listening is a data skill
Imagine these scenarios:
- “I looked at your social media profiles, and decided we should get married.”
- “My phone did a sentiment analysis on your texts - they were 30% negative and I only date people who are 40% positive and above. We should break up.”
Do those sentences look crazy? Businesses do this all the time. We get people’s information, analyze it and subject it to automated decisions based on assumptions that often have no value to the people we are analyzing.
As with any relationship the rule of thumb is this: give them an opportunity to speak, listen to what they are saying and involve them in the decision-making process.
Download this free flowchart poster
POPIA compliance is a challenge. We created this free flowchart poster to help you figure it out. Click below to download your copy.
Download your poster today
SAP Knowledge Sidebar
By Jan van Rensburg
We are in the age of artificial intelligence and machine learning. These technologies aim to do what only humans were able to do in the past. SAP has been heavily promoting their Leonardo platform as an integral part of the intelligent enterprise. These are helpful technologies that can speed up processing, save a tremendous amount in human resources costs and enable organizations to make better decisions. But they are not without their problems. Sample sets can never be perfect, and the machine learning can only be as good as the data it has been trained on. Even worse, some training sets have shown significant bias, including racial bias (e.g. https://blog.algorithmia.com/racial-bias-in-facial-recognition-software/.)
When it comes to applying these technologies in your organization, it’s tempting to optimize processes for time and efficiency by trusting the machines. Both GDPR and POPIA, however, tell us to be careful. The word ‘solely’ in both pieces of legislation is crucial. We can use computers and algorithms to help us make decisions faster, but if these decisions might be substantially consequential for a data subject, you need to build “the human touch” into your business processes and configure your workflows accordingly.
Gericke Potgieter
Gericke is responsible for marketing systems management and data analytics at EPI-USE Labs. He is a qualified ISO 27001 Lead Implementer and has an MA in Socio-informatics (Decision Making Theory). He has spent most of his career in IT, strategy consulting and software development.

